An acute knee injury bursts onto the scene without warning, arriving as a sprain, strain, dislocation, or even a fracture. Often the result of a direct blow or an unexpected twist, this type of injury can transform a routine movement into an agonizing experience.
Medically reviewed by Dr Chaminda Goonetilleke, 31st Dec. 2021
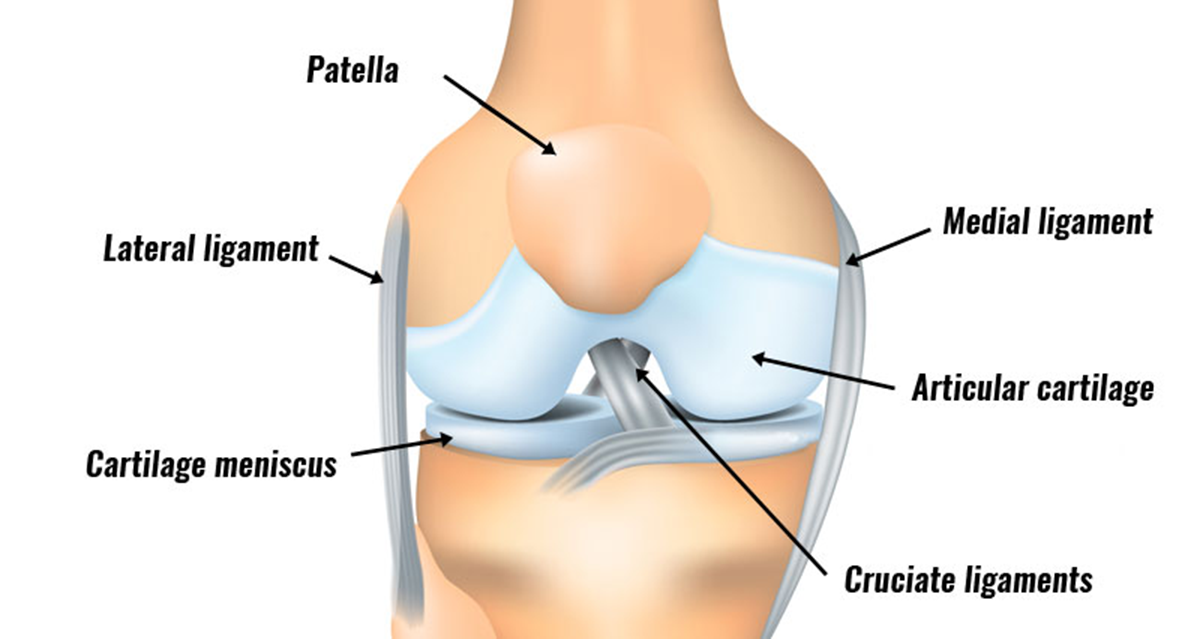
Knee ligament sprains
“Knee Sprain” refers to the tearing of any of the knee’s four ligaments. This injury frequently includes damage to additional joint structures.
Anterior Cruciate Ligament sprain (ACL)
The sprain of an Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) tear often occurs in contact sports that involve swift directional changes.
The symptoms you may experience include:
- Intense knee pain immediately following a collision or a twist in the knee.
- Rapid onset of swelling.
- A sensation or sound of pop or crack in the joint at the moment of injury.
Medial knee ligament sprain (MCL)
A sprain of the Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL), the ligament located inside the knee joint, commonly results from a direct impact or a twist of the knee.
Symptoms include:
- Instantaneous pain localized on the knee’s inner side.
- Swelling that develops rapidly.
- The severity of injuries is categorised into grades one, two, or three.
- Varying degrees of pain, from mild tenderness to severe pain and instability.
Often, MCL sprains coincide with a medial cartilage meniscus injury.
Posterior cruciate ligament sprain (PCL)
A Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) injury involves a tear in the knee joint’s deep ligament. Common causes include an impact on the knee’s front or a twisting motion.
Look out for the following symptoms:
- Pain that emerges immediately, possibly extending into the lower leg.
- Swelling, though it may not always be present.
- A feeling of instability in your knee.
While most PCL sprains undergo conservative treatment, some might necessitate surgery.
Lateral knee ligament sprain (LCL)
A tear in the ligament on the knee’s exterior often results from an inward impact on the knee (propelling the knee outward).
The symptoms, varying in intensity, include:
- Sensitivity on the knee’s outer side.
- Possible swelling, contingent on the severity of your injury.
- With a more severe injury, you may experience a sense of laxity.
Coronary ligament sprain
This type of injury frequently coincides with lateral ligament injuries and shares similar symptoms with a cartilage meniscus injury. Twist movements and directional changes often trigger it.
Here’s what you might experience:
- A sharp, intense pain.
- Tenderness in your knee along the joint line when applying pressure.
- Swelling is unlikely in most cases.
Unhappy triad of the knee
The “Unhappy Triad” of the knee refers to simultaneous damage to three out of the four major knee ligaments, usually resulting from a traumatic injury.
The symptoms to watch for include:
- Intense, severe pain.
- Swelling that develops rapidly.
- An audible tearing sound at the moment of impact.
- Challenges when trying to move the knee.
Knee cartilage injuries
Cartilage injuries refer to the damage inflicted on the smooth, hard articular cartilage located at the bone’s ends or beneath the patella, or an injury affecting the semicircular meniscus.
Medial meniscus tear
A tear in the cartilage meniscus, situated inside the knee, often results from direct impacts and twisting. In some cases, it may progressively develop due to degeneration.
Keep an eye out for these symptoms:
- Immediate pain originates on the knee’s inner side.
- Swelling, which may or may not happen, depends on the severity of the injury or the presence of a concurrent medial ligament tear.
- If the injury is fresh, you might feel tenderness along the joint line inside the knee.
Articular cartilage injury
Damage to the cartilage at the ends of bones may occur due to knee trauma or other injuries. Symptoms to watch out for include:
- Persistent knee pain, inflammation, and swelling.
- Possible ‘locking’ sensation in the joint.
Tendon strains of the knee joint
This refers to a tear or rupture in a tendon, the tissue that connects muscle to bone in the knee.
Patella tendon rupture
A patella tendon tear, also known as a patella ligament rupture, refers to damage in the tissue linking the kneecap (patella) to the shin’s front. Typical causes include jumping or handling an explosive load.
Key symptoms include:
- Intense pain resulting from the rupture.
- A potential popping sound at the time of injury, coupled with swelling, particularly at the patella’s bottom.
- Challenges in bearing weight on the knee or straightening the leg.
Biceps femoris tendon avulsion
This injury involves a torn tendon at the knee’s rear that pulls along a fragment of bone.
The notable symptoms include:
- A sudden sharp pain at the knee’s back typically stops you from continuing any activity.
- Swelling that arises at the injury site, accompanied by tenderness.
- You’ll likely experience hamstring weakness and escalating pain while trying to bend your knee against resistance.
Read more on Biceps femoris tendon avulsion
Hamstring tendon strain
Ruptures—either full or partial—can occur in the tendons that attach to the knee’s back, with the biceps femoris tendon being the most common.
Be alert for the following symptoms:
- A sudden sharp pain in the knee’s back.
- Possible swelling and soreness in the area.
- The area might feel warm at times.
- Pain may resurface when bending the knee against resistance.
Fractures, contusions & dislocations
The conditions below involve either a dislocation or a fracture of the patella (kneecap) or the tibia bone:
Patella dislocation
A kneecap dislocation occurs when the patella shifts from its regular position, typically towards the joint’s exterior.
The key symptoms to watch for include:
- Immediate onset of pain.
- Rapid swelling development within the joint.
- Visible displacement of the kneecap, even though it may quickly return to its original position.
Acute patella injury
A patellar contusion refers to a direct impact or trauma to the kneecap, potentially caused by a knee fall or contact with an opponent.
Look out for these symptoms:
- Sudden, acute knee pain.
- Possible bruising and swelling, coupled with walking difficulties.
- Depending on the injury’s severity, the pain might be confined to the kneecap or extend to the entire joint.
- In case of extreme impact, the patella might fracture.
Knee contusion
Also referred to as a knee bruise, this injury arises from an impact on the knee.
Key symptoms to be aware of include:
- Immediate pain and bruising.
- Tenderness in the impacted area.
- The intensity of symptoms can escalate depending on the severity of the injury.
Dislocated knee
A knee dislocation, a serious injury, occurs when the thigh and shin bones separate.
Notable symptoms include:
- Immediate pain, deformity, along with swift swelling and bruising.
- An inability to put weight on the affected leg.
In such cases, immediate medical attention is crucial.
While the following are not commonly seen causes of acute knee pain, it’s crucial not to overlook them. More serious complications may arise if they remain undiagnosed:
Tibial Plateau Fracture:
- This type of fracture occurs at the top of the shin bone, often during high-speed incidents such as skiing or horse-riding injuries.
- Symptoms include sudden acute knee pain accompanied by joint swelling.
Osteochondral Knee Fracture:
- These fractures often coincide with other injuries, causing immediate pain upon impact, which intensifies when bearing weight.
- Additional symptoms include rapid swelling and a knee joint that may lock and feel unstable.